Anxiety disorders
(Chronic Free-Floating Anxiety)
Anxiety disorders – Definition
Anxiety is a state of dread, tension, and unease. It is considered a normal response to stress or uncertain situations. Feeling anxious for long periods of time or at intense levels may mean that you have an anxiety disorder. You may be diagnosed with an anxiety disorder if the anxiety:
- Occurs without an external threat (called “free-floating” anxiety)
- Is excessive or unreasonable for the situation or threat
- Negatively affects how you function during the day
The most common types of anxiety disorders are:
- Specific phobias
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Social anxiety disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
Anxiety may occur with other conditions, such as alcohol abuse, drug abuse, and depression.
Anxiety disorders – Causes
Anxiety disorders may result from a combination of factors, such as:
- Genetics
- Factors in the environment
Chemical imbalances in the brain (eg, serotonin, norepinephrine) may also play a role.
Anxiety disorders – Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of anxiety disorders include:
- Sex: female
- Family member with anxiety disorders
- Stressful life events
- Poor coping strategies
- History of physical or psychological trauma
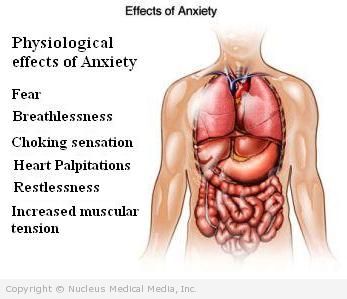
Anxiety disorders – Symptoms
Psychological symptoms may include:
- Worry or dread
- Obsessive or intrusive thoughts
- Sense of imminent danger or catastrophe
- Fear or panic
- Restlessness
- Irritability
- Impatience
- Ambivalence (uncertainty)
- Trouble concentrating
Physical symptoms may include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sweating (especially the palms)
- Dry mouth
- Flushing or blushing
- Muscle tension
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling lightheaded or fainting
- Difficulty sleeping
- Shaking
- Choking sensation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Feeling of “butterflies” in the stomach
- Sexual difficulties
- Tingling sensations
- Nail biting or other habitual behavior
Anxiety disorders – Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A psychiatric evaluation will be done. Your doctor may also do a physical exam and order tests to look for other causes of your symptoms. You may be referred to a psychotherapist for further evaluation.
Anxiety disorders – Treatment
Effective treatment usually involves a combination of interventions, including:
Lifestyle Changes
- Get sufficient rest and sleep.
- If you smoke, quit.
- Reduce or eliminate caffeinated beverages.
- Drink alcohol in moderation.
- Avoid using drugs.
- Reduce exposure to stressful environments.
- Exercise regularly.
Relaxation Techniques
- Practice deep breathing and meditation.
- Learn how to do progressive muscle relaxation.
- Work with a massage therapist.
- Engage in pleasurable activities.
- Do yoga.
Social Support
- Have a strong support system of family and friends.
- Seek therapy to improve your coping skills.
- Join a support group.
Psychotherapy
This therapy addresses thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that play a role in anxiety. It helps you work through traumas and conflicts.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help you identify negative thought patterns and behaviors. Over time, you can learn to retrain your thinking. This will help you choose better options in response to stress and anxiety.
CBT has been very effective in children and teens.
Medication
For severe anxiety or anxiety disorder, medicines may include:
- Benzodiazepines
- Buspirone
- Antidepressants (eg, tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors [SSRIs])
If you are diagnosed with an anxiety disorder, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Anxiety disorders – Prevention
To help prevent anxiety, consider taking the following steps:
- Avoid situations, occupations, and people that cause you stress.
- If unavoidable, confront and overcome situations that provoke anxiety.
- Find a relaxation technique that works for you. Use it regularly.
- Develop and maintain a strong social support system.
- Express your emotions when they happen.
- Challenge irrational beliefs and thoughts that are not helpful to you.
- Correct misperceptions. Ask others for their points of view.
- Work with a therapist.
- Avoid using nicotine or other drugs. If you drink alcohol, drink only in moderation.