Menopause – Definition
Menopause is the time when a woman’s menstrual period ends. Menopause is considered complete when a woman has been without her period for one year. Although menopause can occur anytime between ages 40 to 58, the average age is 51 years old.
Menopause – Causes
Menopause is a natural process. It is caused by a gradual decrease in a hormone called estrogen, made by the ovaries. This period of time when hormones have begun to decrease but menopause has not started is called perimenopause.
When menopause occurs before the age of 40, it is called premature menopause. Factors that may cause premature menopause include:
- Family history of premature menopause
- Autoimmune diseases
- X-chromosome abnormalities
- Medical treatments, such as pelvic surgery, surgical removal of ovaries, chemotherapy, or pelvic radiation therapy
- Medications that lower estrogen levels
- Smoking
Menopause – Risk Factors
Menopause is a natural process associated with aging. You may have a higher risk of premature menopause if you have a family history of it.
Menopause – Symptoms
As menopause approaches, women may have a number of physical and emotional symptoms such as:
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Disturbed sleep patterns, eg, insomnia
- Anxiety
- Mood changes
- Depression
- Dry skin
- Irritability
- Vaginal dryness and pain with sexual intercourse
- Difficulty concentrating
- Trouble remembering things
- Decreased interest in sex
- Frequent urination or leaking of urine
- Headaches
- Achy joints
- Fatigue
- Early morning waking
Menopause – Diagnosis
Your symptoms and medical history will be taken. A physical exam will be done. You may have blood tests, a pelvic exam, and a Pap smear done. Natural menopause is usually diagnosed when a woman has not had a menstrual period for 12 consecutive months.
Menopause may need to be confirmed if it was caused by a surgical procedure. A blood test may be done to look for follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). High levels of FSH (greater than 40) may indicate menopause.
Menopause – Treatment
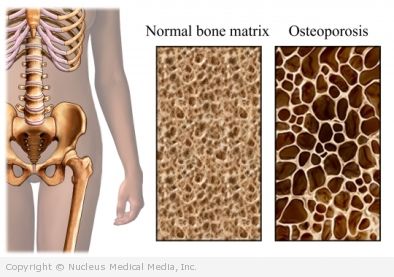
Menopause is a natural part of life. It does not necessarily require treatment. However, symptoms and health risks associated with low estrogen can be treated. These include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and osteoporosis (loss of bone mass).
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Types of hormone replacement therapies include:
- Natural, synthetic, and plant-derived estrogens
- Progesterone
- Combinations of estrogen and progesterone
- Low amounts of male hormones
HRT is available as tablets, gels, skin patches, vaginal rings, vaginal tablets, injections, and pellets inserted into the skin.
There are a number of possible risks associated with HRT such as:
- Endometrial cancer
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Heart disease
- Gallstones
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Healthful Diet
A healthful diet during menopause can improve your sense of well-being. It may also reduce the risk of heart disease, osteoporosis, and certain cancers associated with estrogen. The diet should be low in fat. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. You diet should also include enough calcium and vitamin D.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Caffeine and alcohol may increase your symptoms of anxiety and insomnia. It can also increase your loss of calcium.
Quit Smoking
Smoking can increase the risk of early menopause, heart disease, and osteoporosis.
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise may reduce hot flashes.
Weight-bearing exercises like walking and limbing stairs, and strength exercises may also decrease your risk of osteoporosis.
Stress Management
Stress management may help ease tension, anxiety, and other menopausal symptoms. Deep breathing, massage, warm baths, and quiet music are examples of relaxation techniques.
Over-the-Counter Products
Moisturizers and lubricants are used to help vaginal dryness.
Nonhormonal Medications for Hot Flashes
- Certain blood pressure medicines (taken in lower doses)
- Examples include: clonidine (Catapres), methyldopa (Aldomet)
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Examples include: fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine (Paxil), venlafaxine (Effexor), desvenlafaxine (Pristiq)
- Note: SSRIs and SNRIs should not be used if you are taking tamoxifen (Nolvadex), a medication to reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Menopause – Prevention
Menopause is a natural biologic event that does not need to be prevented. Quitting smoking could slightly delay menopause.