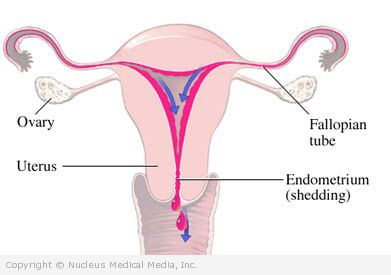
Heavy menstrual bleeding
(Menorrhagia; Hypermenorrhea)
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Definition
Heavy menstrual bleeding (also called menorrhagia) is excessive menstrual blood loss that interferes with a woman’s quality of life.
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Causes
In some cases, the cause is not known. However, many conditions have been associated with menorrhagia, such as:
- Uterine fibroid
- Bleeding disorder (eg, von Willebrand disease)
- Hormonal imbalance
- Cervical or endometrial polyp
- Ovarian cyst
- Certain medicines
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of menorrhagia include:
- Being an adolescent
- Approaching menopause
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Symptoms
Symptoms of menorrhagia include:
- Menstrual bleeding lasting more than seven days
- Unusually heavy bleeding (soaking through a sanitary napkin or tampon every hour)
- Menstrual flow requiring change of sanitary protection during the night
- Menstrual flow including large clots
- Menstrual flow interfering with lifestyle
- Fatigue and/or shortness of breath (symptoms of anemia)
When Should I Call My Doctor?
Call your doctor if you have symptoms of menorrhagia.
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical examination, including a pelvic exam, will be done. Tests may include:
- Pap test
- Blood tests
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Endometrial biopsy (removal of a sample of endometrial tissue)
- Dilation and curettage (scraping of the inner lining of the uterus)
- Hysteroscopy (examination of the cervix and fallopian tubes)
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the heavy menstrual bleeding. Your doctor will work with you to create a treatment plan.
Medications
Your doctor may recommend:
- Hormonal therapy
- An IUD that releases the hormone progesterone
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Iron supplement
Surgical Procedures
In some cases, surgery may be needed, such as:
- Dilation and curettage
- Operative hysteroscopy (may be used along with other tools to remove a polyp)
- Endometrial ablation (removal of the lining of the uterus) — This procedure reduces your chance of becoming pregnant.
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) — After this procedure, you will not be able to become pregnant.
Heavy menstrual bleeding – Prevention
There are no specific steps to prevent this condition.