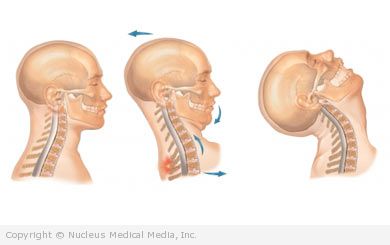
(Cervical Strain and Neck Muscle Sprain)
Whiplash – Definition
Whiplash is a neck injury that includes:
- Spraining the neck ligaments
- Straining the neck muscles
- Bone and nerve injury may be involved
Whiplash – Causes
Whiplash can occur with any sudden, violent, backward jerk of the head or neck that can often occur during:
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Athletic injuries
- Falls
- Assaults
Whiplash – Risk Factors
Risk factors for whiplash include:
- Age: young adults
- Sex: male
- Ankylosing spondylitis (a rheumatic disease that can effect the spine)
Risk factors for poor outcome or longer recovery include being:
- An older woman
- In a truck
- A passenger
- Hit by a moving object
- Hit head-on or perpendicular
- Involved in litigation
- Affected with severe pain or radicular symptoms
Whiplash – Symptoms
The symptoms usually develop over the several hours after the injury. Within 24 hours of the symptoms tend to reach their peak.
Symptoms include:
- Stiff neck
- Neck pain
- Numbness or tingling
- Shoulder pain and stiffness
- Decreased range of neck motion
- Muscle spasms
- Headache
- Pain, numbness, or tingling extending down an arm
Whiplash – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms. You will be asked how the injury occurred. A physical exam will be done. Although most whiplash injuries do not show up on imaging tests, your doctor may choose to order some tests to make sure that no other injuries.
Tests may include:
- Neck x-rays — a test that uses radiation to take a picture of structures in the neck, especially bones
- CT scan — a type of x-ray that uses a computer to make pictures of the bony structures inside the neck
- MRI scan — a test that uses magnetic waves to make pictures of bony and soft tissue structures inside the neck
- CT myelogram — a test that uses dye to better see structures in the neck
- Electrodiagnostic testing — also known as EMG, test muscles
Whiplash – Treatment
Treatment includes:
- Heat or ice packs — Talk with your doctor about using heat or ice to relieve muscle tension and pain. Wrap the heat or ice pack in a towel. Never place it directly on the skin.
- Medications — These may include:
- Pain relievers
- Anti-inflammatories
- Muscle relaxants
- Neck (cervical) collar — This may be given for short-term or occasional use. It will depend upon the extent of injury.
Current belief is that a better recovery can result from earlier activity including:
- Physical therapy — therapy and modalities may help strengthen neck muscles and improve neck motion; exercises may begin within two days of injury
- Mobilization
There is some evidence of the effect of the following:
- Chiropractic — manipulation of the spine done by a chiropractor
- Cervical facet injections
- Radiofrequency neurotomy
- Pulsed magnetic field treatment
If you are diagnosed with whiplash, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Whiplash – Prevention
There are no guidelines for preventing whiplash. It often occurs due to an unexpected event.