(FM; Fibromyalgia Syndrome; FMS)
Fibromyalgia – Definition
Fibromyalgia is a complex, chronic, and disabling disorder. It causes widespread pain and stiffness in the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It also causes poor sleep and fatigue.
Fibromyalgia – Causes
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown.
The following conditions are commonly associated with fibromyalgia:
- Depression and anxiety
- Muscle pain
- Chronic headache, such as tension headaches (frequently beginning with neck discomfort)
- Nocturnal myoclonus (moving legs involuntarily during sleep)
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Complex regional pain syndrome
- Substance abuse
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Female urethral syndrome (irritable bladder)
- Raynaud’s disease
Fibromyalgia – Risk Factors
A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting fibromyalgia. Risk factors include:
- Sex: female
- Age: 20-60 years old
- Physical or mental stress
- Physical trauma (eg, accident, injury, or severe illness)
Fibromyalgia – Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Generalized fatigue or tiredness
- Reduced physical endurance
- Generalized aches and pains of muscles, tendons, and ligaments
- Muscle tightening or spasms
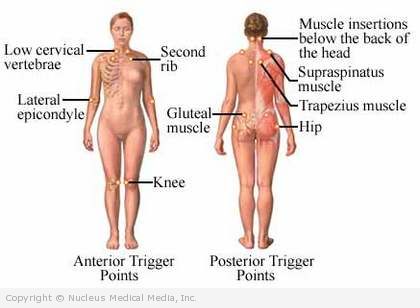
- Pain in specific areas of the body, especially:
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Chest
- Back (upper and lower)
- Hips and thighs
- Insomnia or poor sleep
- Sensations of numbness or swelling (although swelling is not actually present)
- Chronic headaches, including migraines
- Morning stiffness
Factors that may trigger or worsen symptoms include:
- Weather changes, especially cold, damp weather
- Stress or anxiety
- Overexertion
- Medical illness
- Surgery
Fibromyalgia – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. There are no specific tests for fibromyalgia.
The doctor will look for the following signs:
- Widespread pain lasting three months or longer
- Tenderness (on physical exam) in at least 11 of 18 specific areas of the body
Fibromyalgia – Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve or control the symptoms. Treatments include:
Therapy Programs
Physical therapy (gradual aerobic exercise and stretching)
- Heated pool treatments — Aquatic training in warm water (eg, strength, aerobic, and relaxation exercises)
- Applying heat to painful areas
- Alternative treatments, such as massage, acupuncture, relaxation training, trigger point therapy, biofeedback, and yoga
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
Lifestyle Changes
Your doctor may also recommend that you make lifestyle changes, such as:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Learning to cope with physical and mental stress
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule
- Participating in a regular exercise program that includes aerobic activity, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Gentle exercises that may not strain painful areas include walking, biking, and swimming. Talk to your doctor to make sure it is safe for you to start exercising.
Medications
These medicines may help to improve symptoms:
- Antidepressants (eg, amitriptyline, fluoxetine, duloxetine, milnacipran, moclobemide)
- Medicines to relieve pain (eg, acetaminophen, pramipexole, pregabalin, tramadol)
- Sodium oxybate (eg, Xyrem), a central nervous system depressant
Fibromyalgia – Prevention
Because the cause is unknown, there are no guidelines to prevent fibromyalgia.