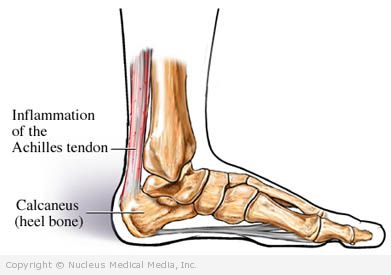
Achilles tendinopathy
(Achilles Tendonitis; Achilles Tendinosis)
Achilles tendinopathy – Definition
Tendinopathy is an injury to the tendon. It can cause pain, swelling, and limit movement. The injuries can include:
- Tendonitis — an inflammation of the tendon (Although this term is used often, most cases of tendinopathy are not associated with significant inflammation.)
- Tendinosis — microtears (tiny breaks) in the tendon tissue with no significant inflammation
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Tendinopathy and the associated pain may take months to resolve.
Achilles tendinopathy – Causes
Tendinopathy is generally caused by overuse of a muscle-tendon unit. Over time, the strain on the tendon causes structural changes within the tendon itself.
Overuse of the Achilles tendon is more common when:
- Increasing your speed or running long distances too quickly
- Suddenly adding strenuous hills or stair climbing to your exercise routine
- Doing too much too soon after taking time away from exercising
- A sudden or violent contraction of the calf muscles, such as during an all-out sprint
- Running too much (overuse)
- Lack of flexibility of the calf muscles
Achilles tendinopathy – Risk Factors
Factors that increase your chance of Achilles tendinopathy include:
- Improper or badly worn footwear
- Improper warm-up for your activity
- Inflexibility of the calf muscles
- Improper cool-down
- An improper training program
Achilles tendinopathy – Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Tenderness — usually located 1-2 inches above the point where the tendon attaches to the heel bone (noticeable in the morning upon rising)
- Stiffness that gradually eases as the tendon is warmed-up
- Pain after activity that gradually worsens
- Radiating or localized pain along the tendon during and/or after running
- Swelling in the area of the Achilles
- Pain at the back of the ankle
Achilles tendinopathy – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and exercise habits. A physical exam will be done.
Your doctor will likely make a diagnosis based on the exam and history. If the symptoms and signs are unclear your doctor may order:
- X-rays — to see if there is calcium in the tendon
- MRI scan — to view areas of interior damage to the tendon
Achilles tendinopathy – Treatment
Rest
Take a break from the activity that caused the tendinopathy. Switch to an activity that doesn’t put stress on the tendon. Avoid uphill and irregular surfaces. Swimming is a good option.
Gradually increase your activity levels. Ice the area for 20 minutes if you have activity related pain.
Orthotics
You may be advised to wear a shoe insert. It will place your foot in the correct position for walking and running.
Physical Therapy
- Stretching
- Massage
- Ultrasound
- Strengthening exercises, focused on the calf muscles
Medications
Some people may benefit from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs). They may be helpful in relieving the pain and decreasing inflammation. This is not curative. It must be combined with other treatment. Topical pain medicines (eg, creams, patches) applied to the skin are another option.
If you are diagnosed with this condition, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Achilles tendinopathy – Prevention
To decrease your chances of getting Achilles tendonitis:
- Take the time to warm-up and cool-down properly.
- Wear appropriate footwear for your sport.
- Do not use shoes beyond the recommended duration. This will depend on:
- How frequently you exercise
- The surface on which you exercise
- The conditions in which you exercise
- Gradually add hill work, stairs, speed, and distance to your routine.
- Stretch and strengthen the calf muscles regularly.