(UC; Colitis, Ulcerative)
Ulcerative colitis – Definition
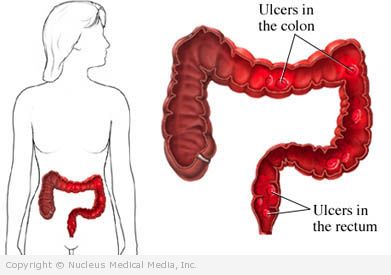
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a type of severe, chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which causes:
- Inflammation
- Ulcers
- Bleeding in the lining of the colon and rectum
Ulcerative colitis – Causes
The exact cause is not known. A virus or bacteria may cause the immune system to overreact and damage the colon and rectum.
Ulcerative colitis – Risk Factors
Having a family member with IBD (includes UC and Crohn’s disease) may increase your risk of developing UC.
Ulcerative colitis – Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps and pain
- Rectal bleeding
- Anemia
- Weight loss
- Fatigue, weakness
- Nausea
- Fever
Ulcerative colitis – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will also be done. Your doctor may order tests, such as:
- Blood tests
- Stool test
- Barium enema
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Biopsy
Ulcerative colitis – Treatment
Treatment options may include:
Dietary Changes
Your doctor may recommend that you avoid certain foods that trigger symptoms, such as:
- Dairy foods (due to lactose intolerance)
- Highly seasoned foods
- High-fiber foods
Talk to your doctor to learn more about the types of foods that you should avoid.
Medications
There are a range of medicines that may be prescribed, such as:
- Aminosalicylate medicines (eg, sulfasalazine, mesalamine, olsalazine, balsalazide disodium)
- Steroid anti-inflammatory medicines (eg, prednisone, methylprednisolone, budesonid)
- Immune modifier medicines (eg, azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, cyclosporine)
- Biological agents (eg, infliximab, adalimumab)
Surgery
Medicine may not cure very severe UC. In some cases, your doctor may suggest surgery. This can involve having all or part of the colon removed. Surgery may also be done because UC increases your risk of colon cancer.
Over time, colitis that is not treated or does not respond to treatment can lead to:
- Arthritis
- Eye inflammation
- Liver disease
- Kidney stones
- Skin rashes
- Osteoporosis
- Colon cancer
If you are diagnosed with ulcerative colitis, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Ulcerative colitis – Prevention
There are no guidelines for preventing this condition.