Peritonitis – Definition
Peritonitis is an inflammation or infection of the peritoneum. The peritoneum is a thin tissue lining that covers the inside of the abdominal cavity. It also covers the outside of the intestines and other abdominal organs.
There are several types:
- Primary
- Secondary
- Peritoneal dialysis related
Peritonitis is a serious condition. It requires immediate treatment. If not promptly treated, it can be fatal.
Peritonitis – Causes
- Primary peritonitis — occurs when there is a buildup of fluid in the abdomen. This is called ascites. It is caused by chronic liver disease, among other conditions.
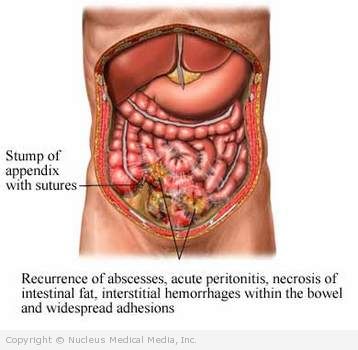
- Secondary peritonitis — caused by bacteria that enter the abdominal cavity. Can be due to an injury or a condition, such as a ruptured appendix.
- Dialysis-related peritonitis — caused by bacteria that enter the peritoneal cavity during or after peritoneal dialysis (a treatment for kidney disease).
Peritonitis – Risk Factors
A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting a disease or condition. Risk factors for peritonitis include:
- Abdominal penetration or trauma
- Immune compromise
- Blood in the abdomen
- Ruptured appendix
- Peptic ulcer
- Colitis
- Diverticulitis
- Gangrene of the bowel
- Pancreatitis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Inflamed gallbladder
- Recent surgery
- Tubes or shunts in the abdomen
- Cortisone drugs
Peritonitis – Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Severe pain or tenderness in the abdomen
- Pain in the abdomen that is worse with motion
- Bloating of the abdomen
- Constipation
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness or dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid pulse or breathing rate
- Dehydration — signs include dry skin and lips, decreased urine production
Peritonitis – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam. Tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Analysis of fluids from the peritoneum
- Abdominal x-rays — to look for signs of inflammation
- Laparotomy — surgery to open and examine the abdomen
Peritonitis – Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause. It may include:
- Surgery to repair openings in the skin surface or to remove damaged tissue
- Antibiotics to treat infection
- Replacement of fluids
If you are diagnosed with peritonitis, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Peritonitis – Prevention
There are no guidelines for preventing peritonitis.