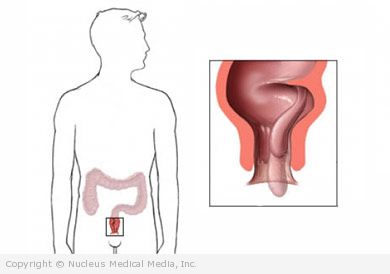
Hemorrhoids – Definition
Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in and around the anus and lower rectum. They stretch under pressure and are similar to varicose veins in the legs. Hemorrhoids are either internal or external.
- Internal (inside) hemorrhoids develop inside the anus. They are painless and sometimes bleed a lot during bowel movements. They may also protrude during bowel movements. If they protrude from the anal opening and cannot be pushed back, they can cause severe pain.
- External (outside) hemorrhoids develop under the skin around the anus and can easily be felt or seen as a lump. They bleed when broken by straining, rubbing, or scratching.
Hemorrhoids – Causes
The exact cause of hemorrhoids is unknown. The major contributing factor appears to be too much pressure on the veins in the rectum. If the pressure continues, the veins become enlarged and protrude.
Hemorrhoids – Risk Factors
A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting a disease or condition. Risk factors include:
- Straining when trying to pass a stool
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Sitting on the toilet for long periods of time
- Pressure on the veins from pregnancy and childbirth
- Advancing age
- Obesity
- Family members with hemorrhoids
- Chronic cough
- Liver disease
- Chronic use of enemas or laxatives
Hemorrhoids – Symptoms
In most cases, symptoms will go away within several days. Although many people have hemorrhoids, not all experience symptoms.
Common symptoms include:
- Bleeding from the anus that may appear:
- On the stool
- On the toilet paper
- In the toilet bowl
- Anal itching and burning
- Swelling and pain during bowel movements
- Sensitive lumps of various sizes around the anus
Hemorrhoids – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. The doctor will examine the anus and rectum to look for swollen blood vessels and perform a digital rectal exam. This is done by inserting a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for abnormalities. Sometimes, it is necessary to do the exam with the use of an endoscope that allows visualizing the rectal canal and other parts of the colon.
Bleeding from the rectum or blood in the stool can be a symptom of other diseases involving gastrointestinal tract or colon/rectal cancer. It is important to see a doctor if you have any rectal bleeding.
Hemorrhoids – Treatment
Initial Treatments
Initial medical treatment of hemorrhoids is aimed at relieving symptoms. Measures to reduce symptoms include:
- Sitz baths — sitting in plain, warm water 2-3 times a day for about 10 minutes each time
- Ice packs — putting cold packs on the anus for short durations to relieve pain and swelling
- Medication — applying hemorrhoidal creams or suppositories to the affected area
- High-fiber diet — Eating more whole fresh fruit, raw, or cooked vegetables, and whole grains has been consistently shown to reduce hemorrhoid symptoms including bleeding. Also, if you enjoy spicy foods, you can continue eating them. Studies have shown that they do not worsen hemorrhoidal symptoms.
- Fluids — drinking 6-8 (8-ounce) glasses of nonalcoholic fluids daily to soften stools
Nonsurgical Procedures
If these treatments provide insufficient relief, one of several nonsurgical procedures may be used to shrink or destroy the hemorrhoidal tissue. These procedures, which are generally performed in a doctor’s office, include:
- Rubber band ligation — a rubber band placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off circulation and force the hemorrhoid to wither away within a few days
- Sclerotherapy — a chemical solution is injected near the blood vessel to cause scarring and shrinkage of the hemorrhoid
- Coagulation therapy — the use of electricity (direct current electrotherapy), laser, or infrared light (photocoagulation) to shrink the hemorrhoidal tissue
Surgery
If nonsurgical procedures are either not an option or fail to resolve the problem, surgical management is the final option:
- Hemorrhoidectomy — This surgery involves permanent removal of hemorrhoids by cutting the hemorrhoidal tissue away. Some of the newest surgical treatments involve using stainless steel staples. While these treatments are favored by many surgeons, there is some evidence that more traditional techniques produce more consistent and long-lasting relief.
If you are diagnosed with hemorrhoids, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Hemorrhoids – Prevention
The best way to prevent hemorrhoids is to keep stools soft so they pass easily. The following practices can help:
- Eat a high fiber diet.
- Exercise regularly, especially walking.
- Empty bowels as soon as possible after the urge occurs.
- Avoid the overuse of laxatives.