(Cutaneous Melanoma; Malignant Melanoma)
Melanoma – Definition
Melanoma is a skin cancer. It affects skin cells called melanocytes. These cells produce skin color. They also give moles their dark color. Under normal conditions, moles are benign skin tumors. This means non-cancerous. Sometimes a mole can develop into melanoma. A new mole may also be an early melanoma.
Melanoma is less common and more dangerous. They are much more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma – Causes
Skin cancer is caused by:
- Ultraviolet radiation from the sun
- Artificial radiation from sun lamps and tanning booths
Melanoma – Risk Factors
These factors increase your chance of developing melanoma:
- Certain types of moles called dysplastic nevi, or atypical moles (which look similar to melanoma)
- Large dysplastic nevi present at birth
- Age: early adulthood, later in life
- Race: white
- Fair skin
- Red or blonde hair
- Light-colored eyes
- Family members with melanoma
- Excessive skin exposure to the sun without protective clothing or sunscreen
- Suppressed immune system
Melanoma – Symptoms
Melanomas are not usually painful. At first they often have no symptoms. The first sign is often a change in the size, shape, color, or feel of an existing mole. They may also appear as a new, dark, discolored, or abnormal mole. Remember that most people have moles. Almost all moles are benign.
The following are signs that a mole may be a melanoma:
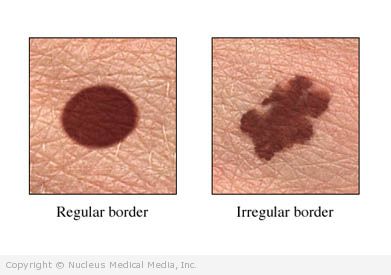
- Uneven shape — one half does not match the shape of the other half
- Ragged edges — ragged, notched, blurred, or irregular; pigment may spread into surrounding skin
- Uneven color — color is uneven with shades of black, brown or tan, and possibly even white, gray, pink, red, or blue
- Change in size — usually growing larger; usually larger than the eraser of a pencil (5 mm or ¼ inch)
- Change in texture — may begin to have fine scales; may become hard or lumpy in advanced cases
- Bleeding — may start to itch or, it may ooze or bleed in more advanced cases
Melanoma – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. The doctor will look at your skin and moles. A biopsy will be taken of certain. Other moles will be watched over time.
The doctor may also examine lymph nodes. They may be in the groin, underarm, neck, or areas near the suspicious mole. Enlarged lymph nodes may suggest the spread of melanoma. The doctor may need to remove a sample of lymph node tissue to test for cancer cells.
Melanoma – Treatment
Once melanoma is found, tests are done to find out if the cancer has spread. Treatment depends on whether the cancer has spread.
Surgery
The melanoma and some healthy tissue around it will be removed. If a large area of tissue is removed, a skin graft may be done. Lymph nodes near the tumor may be removed, as well.
Chemotherapy
This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be given in many forms. This includes pills, injections, and via a catheter.
Biological Therapy
Biological therapy involves substances made by the body to increase or restore the body’s natural defenses against cancer. Examples include:
- Interferon
- Interleukin 2
- Melanoma vaccines
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is the use of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. This is not a cure for melanoma. It is used in combination with other therapies.
Melanoma – Prevention
To reduce your chance of getting melanoma:
- Avoid spending too much time in the sun.
- Protect your skin from the sun. For example, wear a shirt, wide brim hat, and sunglasses.
- Use sunscreens with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15.
- Avoid exposing your skin to the sun between:
- 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m. (standard time)
- 11:00 a.m. and 3:00 p.m. (daylight savings time)
- Avoid sun lamps and tanning booths.
Take the following steps to find melanoma in its early stages:
- See your doctor if you think you have melanoma.
- If you have many moles or a family history of melanoma, have your skin checked regularly for changes in moles.
- Ask your doctor to show you how to do a skin self-exam. Do self-exams to look for any new or changing moles.