(Acute Bronchitis; Lower Respiratory Tract Infection)
Bronchitis – Definition
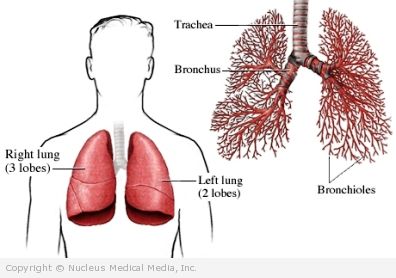
Air passes to the lungs through airways called bronchi. Bronchitis is swelling of the bronchi. It can make breathing difficult.
There are different types of bronchitis such as:
- Acute bronchitis — This is a sudden onset of symptoms. It only lasts a short time with a full recovery of lung function.
- Chronic bronchitis — This is a serious, long term condition. It causes blockage and damage of the lungs. It is often the result of many years of cigarette smoking.
This fact sheet focuses on acute bronchitis.
Bronchitis – Causes
The swelling in the bronchi may be caused by:
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Smoking (cigarettes or marijuana)
- Breathing in certain irritants (usually in work setting) such as:
- Ammonia
- Chlorine
- Minerals
- Vegetable dusts
Bronchitis – Risk Factors
Risk factors for bronchitis include:
- Having a cold or flu
- Contact with a person with a respiratory viral or bacterial infection
- Smoking
- Exposure to second-hand smoke
- Asthma
- Exposures to respiratory inhalants at work
- Poor functioning immune system
Bronchitis – Symptoms
Symptoms of acute bronchitis may include:
- Cough
- Increased sputum production
- Trouble breathing
- Wheezing
You may also have other cold or flu symptoms such as slight fever, sore throat, and nasal congestion.
Bronchitis – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done.
Tests are rarely needed. The following may be recommended if the bronchitis is severe or the diagnosis is not clear:
- Blood test
- Chest x-rays — to check for other conditions such as pneumonia
- Sputum cultures to check for the presence of unusual bacteria
Bronchitis – Treatment
Treatment is aimed at relieving the symptoms. Your doctor may recommend:
- Ibuprofen or acetaminophen to treat pain and fever
- Note : Aspirin is not recommended for children or teens with a current or recent viral infection. This is because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Ask your doctor which other medicines are safe for your child.
- Expectorants or cough suppressants
- There are some concerns about the safety of over-the-counter cough and cold products in children. The FDA recommends that these products should not be used in children less than 2 years old and supports not using them in children less than 4 years old.
- Albuterol to help open airways if there are signs of breathing difficulty
- Herbs and supplements — Pelargonium sidoides extract may help resolve symptoms in patients with acute bronchitis
- Increased fluid intake
- Cool mist humidifier — to ease breathing
Antibiotics will not be helpful if the infection is caused by a virus. Most of these infections are caused by viruses.
If you are diagnosed with bronchitis, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Bronchitis – Prevention
To reduce your chance of getting bronchitis:
- Avoid contact with people who have respiratory viral or bacterial infections.
- Stop smoking or never start.
- Avoid passive smoke.
- Avoid exposure to irritants in the air.