Chickenpox – Definition
Chickenpox is a viral infection. It is highly contagious. It creates a widespread itchy rash. In some, the infection can also cause serious complications. The infection is more dangerous for adults and newborns. It is also a danger for people with suppressed immune systems.
Chickenpox – Causes
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV). It spreads from person to person via:
- Airborne droplets of moisture containing the VZV virus
- Direct contact with fluid from a chickenpox rash
It is contagious 1-2 days before the rash erupts. It remains so until all of the blisters have crusted five days later. It is most contagious just after the rash has broken out.
A pregnant mother can transmit virus to fetus.
Chickenpox – Risk Factors
Factors that increase your chance of getting chickenpox include:
- Close contact with an infected person (unless you’ve been vaccinated or have already had chickenpox)
- Age: less than three years old with peak incidence between 5-9 years old
- Immune deficient state (eg, leukemia, organ transplantation, high-dose steroid, HIV)
- Cancer
- Pregnancy
- Time of year (late winter, early spring)
Chickenpox – Symptoms
Symptoms break out about 10-21 days after contact. They are more severe in adults than they are in children.
Initial symptoms include:
- Mild headache
- Moderate fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Severe itch
- Lack of appetite
- General feeling of malaise
- Some children complain of abdominal pain
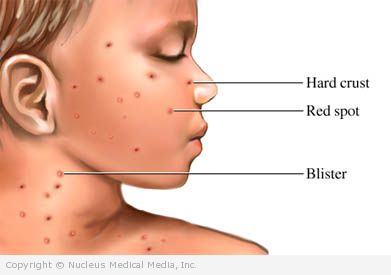
The rash appears within 1-2 days after the first symptoms. The rash will:
- At first consists of small, flat, red spots
- Spots become raised and form a round, intensely itchy, fluid-filled blister
- Blisters develop in clusters, with new clusters forming over 5-6 days
- Usually develop into crops on the skin above the waist, including the scalp
- May also appear on the eyelids, in the mouth, upper airway, voice box, or on the genitals
- Typically crusts over by day six or seven and disappears within three weeks
Chickenpox – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Diagnosis is usually made on the basis of age and the rash. Blood and lab tests to identify the virus are rarely needed.
Chickenpox – Treatment
In most people, chickenpox is mild. It will naturally run its course. In these cases, treatment focuses on relieving the symptoms.
To Reduce Itching
- Wet compresses on the skin
- Nonprescription anti-itch creams or lotions
- Oatmeal baths
- Oral antihistamines (eg Benadryl)
- Note : Aspirin is not recommended for children or teens with a current or recent viral infection. This is because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Ask your doctor which other medicines are safe for your child.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics can not cure infections caused by a virus. They may be given if the rash becomes infected with bacteria.
Antiviral Medication
The course, severity and duration of the infection may be reduced by antiviral medications such as:
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
They are often used in:
- Adolescents, adults, and individuals with compromised immune systems
- Individuals with chronic skin or lung diseases and those taking aspirin or steroids
Special Needs
Varicella-zoster immune globulin is often given immediately after exposure. It is reserved for newborns and people with weak immune systems.
Chickenpox – Prevention
Avoid contact with anyone who has chickenpox. This is very important if you have not been vaccinated against the infection.
Vaccination in Children
The varicella vaccine or a combination vaccine called MMRV (protects against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella) is recommended for most children.
There is a “catch-up” schedule if your child has missed the routine injections.
Vaccination in Adults
Adults who have never received the varicella vaccine or have never had chickenpox should also be vaccinated.
Vaccination After Exposure
If you or your child has not been vaccinated but has been exposed to chickenpox, a vaccine given right away may help lessen the severity of the infection or prevent it.