Ingrown toenail
Ingrown toenail – Definition
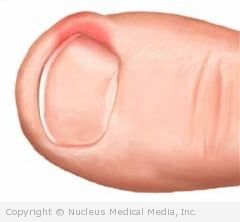
An ingrown toenail happens when a portion of the toenail curves into the flesh of the toe and imbeds itself in the soft tissue. It can occur on any of the toes, but usually occurs on one of the big toes.
Ingrown toenail – Causes
The most common causes of an ingrown toenail are:
- Improper cutting or trimming of the toenail (rounding the edges of the nail rather than cutting the nail straight across)
- Wearing footwear that is too tight
- Repeated trauma to the toes (toe jamming), often due to sports activities
Ingrown toenail – Risk Factors
A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting a disease or condition. The main risk factor for ingrown toenails is having family members with ingrown toenails.
Ingrown toenail – Symptoms
Ingrown toenails often cause no symptoms at first. Eventually, the following symptoms may develop at the site of the ingrown toenail:
- Pain (sometimes severe)
- Redness
- Swelling
- Warmth
- Pus draining from the area
Ingrown toenail – Diagnosis
In almost all cases, you or your doctor can diagnose an ingrown toenail based on the location and the symptoms. In rare cases, you may need an x-ray. For example, if your doctor suspects the infection may have spread to the toe bone.
Ingrown toenail – Treatment
You may be able to treat an ingrown toenail yourself if you catch it early. But if the condition gets worse or does not improve, you will need to seek medical care. If you have diabetes, you must seek medical attention for any infection or wound involving your feet or toes.
Medical Care
Your doctor may recommend the following treatments:
- Oral antibiotic medication
- Removing the ingrown portion of the toenail
- Draining the area that has become infected
- Using a splint to lift the corner of the nail away from the soft tissue of the toe
If you repeatedly get ingrown toenails, or your ingrown toenail is severe, the doctor may:
- Remove a portion of the toenail and apply medicine to the site to prevent that portion of the nail from growing back
- Remove the entire toenail so that the nail will not grow back
Self-care
- Wear open-toed shoes or sandals until the pain and swelling of the nail subside. This will reduce any pressure on the toenail.
- Soak your foot in warm water for 15 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day.
- After soaking, dry your foot and toe thoroughly.
- As the toenail grows out, cut it straight across.
- Promptly seek medical care for an ingrown toenail if you have any of the following conditions:
- Fevers
- An ingrown toenail that is severe, worsening, or not getting better
- Diabetes
- Age: over 50 years old
- Circulatory problems
- A disorder of your immune system
- Any other chronic health problem
Ingrown toenail – Prevention
To help prevent ingrown toenails:
- Cut your toenails straight across and avoid rounding the edges. The corner of the nail should be visible above the skin of your toe.
- Wear shoes and socks that fit properly and are not too tight.
- Keep your feet clean.
- Keep your feet dry by wearing cotton socks and/or using foot powder.