(ED; Erectile Dysfunction; Male Erectile Disorder)
Impotence – Definition
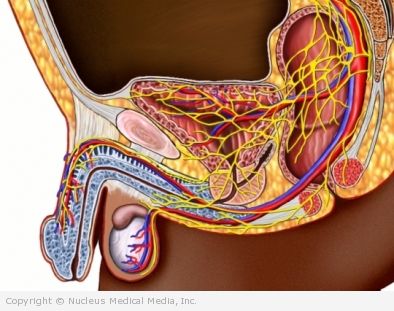
Impotence is the inability to attain or maintain an erection of the penis that is firm enough for sexual intercourse.
To initiate and maintain an erection, the penis must fill with blood. One type of blood vessels open wide to allow blood into the penis. Meanwhile, a second type of blood vessel squeezes down, this will keep the blood from leaving the penis. Nerve signals cause the proper changes in the blood vessels.
Impotence – Causes
The following factors can cause erectile dysfunction:
Venous Leak
The blood vessels that keep the blood from leaving the penis may be injured or have disease. This can cause a leak in these vessels. Blood can escape through these leaks during an erection. This means that an erection cannot be made or may not last long.
Neurovascular Function
Problems with the nerves and blood vessels can cause impotence. Conditions that can cause problems include:
- Nerve dysfunction — can reduce feeling in the penis, resulting in impotence
- Diabetes — interferes with nerve signals
- Complete loss of nighttime erections
- Hardening of the arteries — can cause reduced blood flow
- Peripheral neuropathy, spinal cord injury, and surgery — can damage nerves
- Side-effects from medications
Psychological Factors
Many of the nerve signals needed for an erection come from the brain. Emotional problems may play a role in men who suddenly develop impotence.
Impotence – Risk Factors
Factors that increase your chance of developing impotence include:
- Age: 65 and older
- Race: Hispanic
- Obesity
- Medical conditions:
- Diabetes
- Hardening of arteries
- Chronic kidney disease
- Liver failure
- Peyronie’s disease (bending of the penis caused by scar tissue)
- Endocrine disorders
- Neurological disorders (eg, multiple sclerosis, peripheral neuropathy, stroke)
- Hypertension
- Psychiatric disorders (eg, anxiety, depression)
- Traumatic conditions:
- Vascular surgery
- Pelvic surgeries (particularly for prostate cancer)
- Spinal cord injury
- Behaviors:
- Alcohol use
- Illegal drug use
- Anabolic steroid use
- Heavy smoking
- Interpersonal conflicts with a sexual partner
- Medications:
- Antihypertensives — for high blood pressure
- Antihistamines — common as allergy medication
- Antidepressants
- Tranquilizers
- Antipsychotics
Impotence – Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- A less firm penis
- Fewer erections
Impotence – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Expect questions about the frequency, quality, and duration of your erections. Your answers may help the diagnosis.
The doctor will examine your penis, testes, and rectum. If a physical cause is suspected, you will need lab tests, including:
- Hormone levels such as thyroid function tests
- Prolactin levels
- Testosterone levels
Nocturnal Penile Tumescence Testing
This test will monitor erections while you sleep. Involuntary erections during sleep are normal. If you have impotence but have normal erections during sleep, the problem may be emotional. If you have problems with an erection even while you sleep, the problem may be physical.
Imaging
Doppler imaging is used to look at the blood flow. The test is done to check for bloodflow in the penis. It will also look for blockage in the arteries or veins that supply the penis.
Impotence – Treatment
Treatment options include:
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe:
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors, such as:
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
- Do not take these medications if you are also taking nitrates.
- Oral testosterone, if you have low testosterone levels
- Alprostadil, either injected into the penis or inserted into the urethra as a suppository
Use caution and talk to your doctor before taking any over-the-counter medicines for impotence. Some of them may be unsafe.
Vacuum Devices
A vacuum device pulls blood into the penis. A band will then be placed around the penis to keep the erection. A vacuum device may include:
- Plastic cylinder for the penis
- Hand pump for pumping air out of the cylinder
- Elastic band for holding the erection after removal of the cylinder
Vascular Surgery
Vascular surgery is done to repair the blood vessel leaks. This has been shown to be effective in some cases.
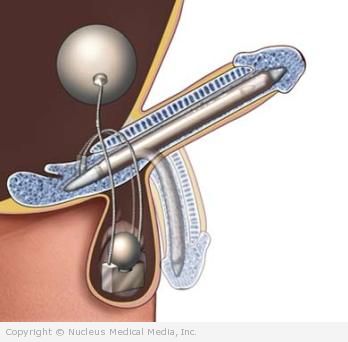
Penile Implants
Implants may be placed in the penis. This implants can be inflated to simulate and erection.
Sex Therapy
Sex therapy may help impotence resulting from:
- Ineffective sexual techniques
- Relationship problems
- Anxiety
- Depression
Impotence – Prevention
To reduce your chance of becoming impotent:
- Take medications to manage blood pressure, diabetes, or depression.
- Ask your doctor about changing medications.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat a healthful diet.
- If you smoke, quit. Smoking is significantly associated with impotence in middle-aged and older men.
- Talk to a therapist or counselor.