Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy – Definition
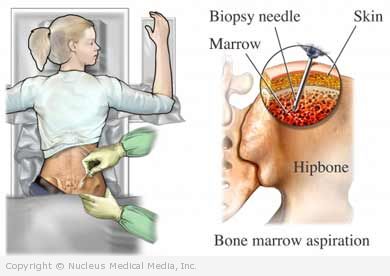
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of a sample of bone marrow. The sample is sent for testing. The procedure is most often done on the pelvic bone, but it may also be done on the sternum.
Bone marrow biopsy – Reasons for Procedure
A bone marrow biopsy may be done to:
- Evaluate unexplained low red blood cell count ( anemia), low white cell count (leucopenia), or low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- Diagnosis and staging of lymphoma (tumors of the lymphoid tissues) or solid tumors
- Diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation of leukemias
- Evaluate iron level problems
- Investigate unexplained spleen enlargement (splenomegaly)
- Evaluate other blood disorders
Bone marrow biopsy – Possible Complications
Complications are rare, but no procedure is completely free of risk. If you are planning to have this procedure, your doctor will review a list of possible complications which may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
Some risk factors for complications during this procedure include:
- Bleeding disorders
- Infection of the skin at the biopsy site
- Infection in the bloodstream
- Previous radiation treatment to the biopsy site
- Severe osteoporosis
Bone marrow biopsy – What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
Your doctor may perform a physical exam and blood tests.
Talk to your doctor about your medicines. You may be asked to stop taking some medicines up to one week before the procedure, like:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plavix) or warfarin (Coumadin)
Bone marrow biopsy – Anesthesia
Local anesthesia will be used. It will numb the area.
Bone marrow biopsy – Description of Procedure
You may be given a light sedative. It will help you relax. The biopsy area will be cleaned and numbed.
A hollow biopsy needle will be inserted into the bone. The needle will be twisted and advanced. This motion will allow a sample of bone marrow to enter the core of the needle. The doctor may need to use a fair amount of pressure and may need to rock the needle. The needle will then be removed. The bone marrow sample will be inside the needle. Pressure will be applied over the puncture area. A bandage will be applied.
Bone marrow biopsy – Immediately After Procedure
The bone marrow specimen will be examined by a pathologist. Ask your doctor when to expect the results.
Bone marrow biopsy – How Long Will It Take?
About 30 minutes
Bone marrow biopsy – Will It Hurt?
The injection of anesthesia may sting or burn. You may notice a sensation of pressure and/or pain when the biopsy needle is rocked. Once the biopsy is done, you may feel soreness in the area for a few hours.
Bone marrow biopsy – Post-procedure Care
At Home
You should be able to resume your normal activities after your biopsy. If you have had a sedative, avoid driving or operating equipment until the effects of the medicine have worn off.
Be sure to follow all of your doctor’s instructions.
Bone marrow biopsy – Call Your Doctor
After arriving home, contact your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Redness, swelling, increasing pain, excessive bleeding, or any discharge from the biopsy site
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain
- Joint pain, fatigue, stiffness, rash, or other new symptoms
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.