Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis – Definition
Amniotic fluid surrounds the baby during pregnancy. Amniocentesis is the removal of a small amount of this fluid for testing.
Amniocentesis – Reasons for Procedure
Amniocentesis is most often done to see if there is an abnormality in your baby’s genes (DNA). It can also be done to see if your baby is developing correctly.
Factors that indicate that you may need this procedure include:
- Age: over 35 years old (at the time of delivery)
- Family history of chromosome abnormality
- Family history of inherited disorder
- Family history of neural tube defect (problems in spine and brain growth, such as spina bifida or anencephaly)
- Abnormal results from an earlier blood screening test, such as maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
Depending on your risk factors, cells in the amniotic fluid are tested for:
- Chromosome abnormalities. The results are usually ready within 14 days. Missing or extra chromosomes lead to physical birth defects and intellectual disability, such as Down syndrome.
- Inherited genetic diseases — Test results are usually ready in 1-5 weeks. Examples include:
- Tay-Sachs disease — most frequent in the Ashkenazi Jewish population
- Cystic fibrosis — most frequent in Caucasians of northern European ancestry
- Sickle cell disease — most frequent in the Black population
Amniocentesis may also be done:
- To determine whether the baby’s lungs are mature
- In high risk pregnancies that may require early delivery
Amniocentesis – Possible Complications
Complications that may occur with an amniocentesis include:
- Miscarriage — less than 1% risk
- Bleeding, cramping, and leaking fluid from the vagina
- Infection
- Mixing of blood if you and your baby have different blood types
- Need for repeat testing
- Harm to the fetus by needle (rare)
Factors that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Maternal obesity
- Previous abdominal surgery
Be sure to discuss these risks with your doctor before the procedure.
Amniocentesis – What to Expect
Anesthesia
Your doctor may give you local anesthesia. This numbs a small area in the abdomen where the needle will be placed.
Amniocentesis – Description of the Procedure
This is usually done when you are 16 weeks pregnant. It is done later in the pregnancy when checking your baby’s lung maturity.
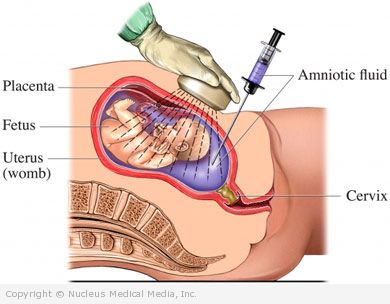
First, your doctor will do an ultrasound. This will help to choose a safe spot to insert the needle. Your abdomen will be cleaned. Next, the doctor will insert a very thin needle through the abdomen into the uterus. A few teaspoons of amniotic fluid will be taken out. After the needle is removed, the doctor will make sure that your baby’s heartbeat is normal. In most cases, an ultrasound will be used throughout the procedure.
Amniocentesis – How Long Will It Take?
About 45 minutes.
Amniocentesis – Will It Hurt?
You may feel cramping when the needle enters your abdomen. You may also feel pressure when the fluid is withdrawn.
Amniocentesis – Post-procedure Care
When you return home after the procedure, do the following to help ensure a smooth recovery:
- For the first few hours, avoid physical stress.
- Rest for the first 24 hours, avoiding heavy exercise and sexual activity for 24 hours.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions.
Although a test showing a healthy baby is ideal, you will need to be prepared if the results show otherwise. If the test shows that your baby may have a genetic disorder, you may need to make tough decisions regarding your pregnancy. If you do continue with the pregnancy, then you will need to address your child’s special needs. Your doctor can help you understand the pros and cons of having this test, as well as work with you on options that are best for you once you know the results.
Amniocentesis – Call Your Doctor
After arriving home, contact your doctor if you have:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pain or cramping in the lower abdomen or shoulder
- Vaginal bleeding or a loss of fluid from the vagina
- Redness, swelling, increasing pain, excessive bleeding, or discharge from the amniocentesis site
- New, unexplained symptoms
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.