Rosacea – Definition
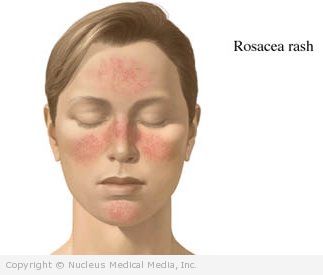
Rosacea is a skin disorder. It causes chronic redness of the face. It can also cause swelling, tiny pimples, and the appearance of broken blood vessels. Rosacea usually affects the cheeks, forehead, chin, and nose. The ears, chest, and back may also be affected. More than half of people with rosacea also have mild eye symptoms. This may include redness, burning, and watering. This is known as ocular rosacea.
Rosacea – Causes
The cause of rosacea is unknown. Several theories exist. Factors that can cause flushing or blushing may trigger flare-ups in people with rosacea.
These factors include:
- Very hot or spicy foods
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Sun exposure
- Extreme temperatures (very hot or very cold)
- Exercise
- Emotional stress or social embarrassment
- Rubbing, scrubbing, or massaging the face
- Irritating cosmetics and other toiletries
Rosacea – Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk for rosacea include:
- Sex: female
- Age: between 30 and 60 years old
- Fair skin
- Having family members who have rosacea
Rosacea – Symptoms
The symptoms of rosacea vary from person to person. They include:
- Frequent flushing on the face and neck
- Redness and swelling on the face
- Small pink bumps and/or pimples
- Thin red lines showing the small blood vessels of the face
- Redness, burning, dryness, and tearing of the eyes
- An enlarged, bulbous red nose (less common, affecting men more than women)
Rosacea – Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Your skin will also be examined. You may be referred to a doctor who specializes in skin disorders. This type of doctor is called a dermatologist. Do not try to diagnose or treat yourself. Certain over-the-counter medications could make your condition worse.
Rosacea – Treatment
Rosacea generally can’t be cured. It can be controlled. There are several ways to manage rosacea. Your doctor may recommend more than one, depending on your condition.
Medications
Prescription medications for rosacea include:
- Antibiotics applied to the skin
- Other topical treatments such as azelaic acid, sulfa, or tretinoin (Retin-A)
- Antibiotics taken by mouth
In more severe cases, medications may sometimes include:
- Oral isotretinoin (Accutane)
- In very rare more severe recalcitrant cases, oral methotrexate, dapsone, primaquine, chloroquine, or prednisone
*Topical cortisone is generally avoided on the face. It can make rosacea worse in the long run. It can be effective as very short-term treatment.
Treatment for redness or flushing may include:
- Clonidine in low doses
- Beta blockers (certain types)
Surgery
The following procedures minimize redness, enlarged blood vessels, and an enlarged nose:
- Electrosurgery — uses a tiny electric needle
- Laser surgery — uses a laser
Rosacea – Prevention
Preventing rosacea can be difficult. If you have rosacea, there are several steps you can take to control the condition:
- Avoid things that may trigger flushing or blushing. This includes certain foods, alcohol, and exposure to the sun.
- Protect your skin from the sun. Use clothing, hats, or sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 15 or higher.
- Exercise in a cool environment to avoid overheating.
- Avoid anything that irritates your skin:
- Apply topical medications, moisturizers, and cosmetics very gently
- Use cleansers, moisturizers, cosmetics, and other toiletries that are gentle and alcohol-free