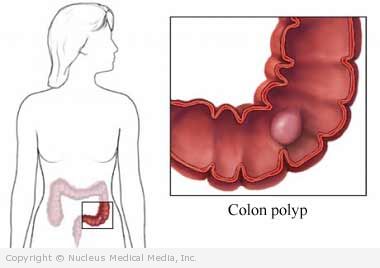
Colon polyps – Definition
Colon polyps are growths on the lining of the colon or rectum. The colon and the rectum are parts of the large intestine. It is all part of the digestive system.
The two most common kinds of polyp are:
- Adenomatous polyps — can become larger over time and may develop into cancer
- Hyperplastic polyps — do not increase in size and only rarely become cancerous
Colon polyps – Causes
The cause of colon polyps is unknown. It may be partly due to hereditary factors. There is a genetic condition called polyposis coli. It causes thousands of adenomatous polyps throughout the bowel.
Colon polyps – Risk Factors
Risk factors for colon polyps include:
- Age: over 50 years
- Family members with colon polyps or colon cancer
- History of colorectal cancer (or cancer of the large intestine)
- Weight gain and obesity
Colon polyps – Symptoms
Symptoms are often not present. Polyps are only found during an endoscopy or x-ray. If symptoms are present, they can include:
- Rectal bleeding
- Anemia
- Diarrhea, constipation, and/or bloating that lasts over a period of time
- Abdominal pain, rarely
Colon polyps – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Tests may include:
- Digital rectal exam — the doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel for polyps.
- Stool test — a sample of your stool is checked for blood.
- Sigmoidoscopy — a thin, lighted, flexible tube is inserted into the rectum to examine the rectal area and the lower colon.
- Colonoscopy — a thin, lighted, flexible tube (longer than a flexible sigmoidoscopy tube) is inserted in the anus and used to view the entire colon.
- Barium enema and x-ray — a barium fluid is injected into the colon and rectum. Several x-rays are taken. The barium makes your colon show up on x-ray.
- Biopsy — a sample of tissue is removed for testing. It is sent to a lab to determine whether the polyp is adenomatous or hyperplastic. It will also be checked for cancer cells.
Colon polyps – Treatment
Depending on the size of the polyp, it may be removed. Large polyps are at high risk for becoming cancerous. They should be removed. Usually, polyps can be removed by colonoscopy.
If the polyps are very large, you may need to have surgery to have them removed. Your doctor may send the tissue from the removed polyps to be tested for cancer.
Colon polyps – Prevention
It’s not clear how polyps can be prevented. However, the following guidelines can help you stay healthy and may help prevent not only polyps but also colon cancer:
- Eat a high fiber diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Minimize the amount of animal fat in your diet. This occurs in beef and other meat products as well as full-fat dairy products.
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Don’t smoke.
- See your doctor for regular screenings after the age of 50.
- More frequent screenings may be needed if polyps are found.