(Urethral Infection)
Urethritis – Definition
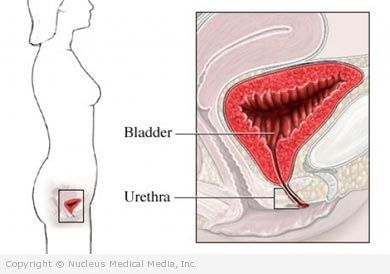
Urethritis is an inflammation, infection, or irritation of the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body from the bladder.
Urethritis – Causes
Urethritis is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, including:
- Organisms that cause bladder or kidney infections:
- E. coli
- Klebsiella
- Organisms that cause sexually transmitted diseases (STDs):
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Viruses such as herpes simplex, cytomegalovirus, or human papillomavirus
- Other bacteria:
- Ureaplasma urealyticum
- Mycoplasma genitalium
Urethritis – Risk Factors
Risk factors that increase your chance of getting urethritis include:
- Sex: female
- Multiple sexual partners
- Recent change in sexual partners
- Unprotected sex (without use of a condom)
- History of other STDs
- Bacterial infection of other parts of the urinary tract (bladder, kidney, prostate)
- Medications that lower resistance to bacterial infection
- Having catheters or tubes placed in the bladder
- Acidic foods
- Spermicides
Urethritis – Symptoms
People with urethritis may not have symptoms, especially women. Approximately 50% of men infected with Chlamydia trachomatis have no symptoms.
Symptoms may include:
- Pain and/or burning while urinating
- Blood in the urine
- Increase in urinary:
- Frequency
- Urgency
- Itching, swelling, and/or tenderness in the groin
- Pain during intercourse
- In men:
- Discharge from the penis
- Blood in the semen
- Pain during ejaculation
- Swollen and/or tender testicles
If left untreated, urethritis can spread and cause infection in other parts of the urinary tract such as the bladder, ureters, or kidneys.
Urethritis – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. It will include a pelvic exam. Urethritis is usually diagnosed from its symptoms. Tests to confirm the diagnosis and identify the organism causing the condition may include:
- Urethral swab for microscopic study or culture
- Blood and urine tests
- Specific tests for Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, or other STDs
Urethritis – Treatment
Urethritis is usually treated with medication. The type of medication will depend on the cause of the urethral infection:
- Antibiotics — to treat urethritis caused by bacteria
- Antiviral drugs — to treat urethritis caused by a virus
If urethritis is caused by an STD, all sexual partners should be tested and treated.
Urethritis – Prevention
Steps to prevent urethritis include:
- Practicing safe sex by using condoms and barrier methods of contraception
- Urinating immediately after having sexual intercourse
- Treating all sexual partners who are infected or exposed
- Regularly drinking plenty of fluids, including cranberry juice