Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease – Definition
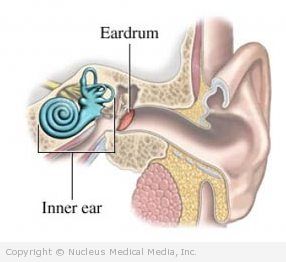
Meniere’s disease is a disorder of the labyrinth in the inner ear. The labyrinth is a system of cavities and canals in the inner ear that affects hearing, balance, and eye movement.
Meniere’s disease – Causes
An increase in the volume or pressure of fluid in the labyrinth can result in Meniere’s disease. The cause of these fluid changes is unknown. Possible causes may include:
- Part of the labyrinth ruptures, allowing fluid in different compartments to mix
- Scar tissue causes a blockage in the labyrinth
- Inner ear injury due to:
- Viral infection
- Syphilis, a sexually-transmitted disease
- Autoimmune disorders
- Blood vessel problems
- High cholesterol or other fats in the blood
- Hormonal disorders
- Medications, such as antibiotics and chemotherapy agents
Meniere’s disease – Risk Factors
A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting a disease or condition. Risk factors for Meniere’s disease include:
- Age: 20 to 60
- Race: Caucasian
- Family history of Meniere’s disease
- Stress
- Allergies
- Excess salt in the diet
- Excess noise
Meniere’s disease – Symptoms
The intensity of symptoms can vary from one person to another. Symptoms usually come on suddenly. They typically involve only one ear, but may involve both.
- Symptoms may include:
- Episodes of vertigo (spinning sensation), often accompanied by:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sweating
- Paleness of the skin
- Weakness or falling
- In some cases, headache or diarrhea
- Hearing loss may worsen during attacks of vertigo
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Poor sense of balance
- A tendency for symptoms to worsen with movement
Meniere’s disease – Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam. This will include an examination of your ears and a neurologic exam to evaluate for possible nerve damage.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests — to check for an underlying cause
- Hearing test — this is also called an audiometry
- Electronystagmogram — a type of eye movement test
- Auditory brainstem response — measures electrical activity in the hearing nerve and brain stem
- Electrocochleogram — measures electrical response of the inner ear to sound
- MRI scan — a test that uses magnetic waves to make pictures of structures inside the ear
Meniere’s disease – Treatment
Treatment may include:
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes
These may help limit symptoms:
- Bed-rest during acute attacks of vertigo
- Avoid foods that are high in salt and high in sugar
- Drink adequate fluids
- Promptly begin replacing fluids lost to heat or exercise
- Avoid caffeine, aspirin, and smoking
- Minimize stress
- Avoid medications that seem to bring on or worsen symptoms
- Consider a hearing aid, if necessary
- Consider masking devices (white noise) to limit the effects of tinnitus
- Take safety measures to avoid falling
- Restrict chocolate consumption
- Reduce alcohol intake
Vestibular Exercises (Vestibular Rehabilitation)
Your doctor may suggest specific vestibular exercises. These exercises use a series of eye, head, and body movements to get the body used to moving without dizziness. You may work with a physical therapist to learn these.
Medications
Medications include:
- Drugs to treat vertigo, such as meclizine or scopolamine
- Antiemetics — medications to help control nausea
- Other medications that may improve hearing, control inner ear swelling, or limit overall symptoms, including:
- Antihistamines
- Cortisone drugs for a short time
- Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications
- Diuretics
- Aminoglycoside therapy (such as streptomycin or gentamicin) to permanently destroy the part of the inner ear that deals with balance
Surgery
Surgical procedures are not always helpful, and include:
- Endolymphatic sac decompression — removal of a portion of inner ear bone and placing a tube in the inner ear to drain excess fluid
- Labyrinthectomy — destruction or removal of the entire inner ear, which controls balance and hearing
- Vestibular nerve section
Meniere’s disease – Prevention
There are no specific guidelines for preventing Meniere’s disease. However, to help reduce your risk, avoid the following risk factors:
- High-salt diet
- High-sugar diet
- Excess noise
- Excess alcohol
- Stress
- Smoking
- Use of drugs that can be toxic to the ear such aminoglycosides, aspirin, and quinine